IBL News | New York
Google introduced yesterday on Chrome — on browser release M121 — experimental generative AI features.
These features will be available in Chrome on Macs and Windows PCs over the next few days, starting in the U.S.
“Because these features are early public experiments, they’ll be disabled for enterprise and educational accounts for now,” said Parisa Tabriz, Vice President of Chrome.
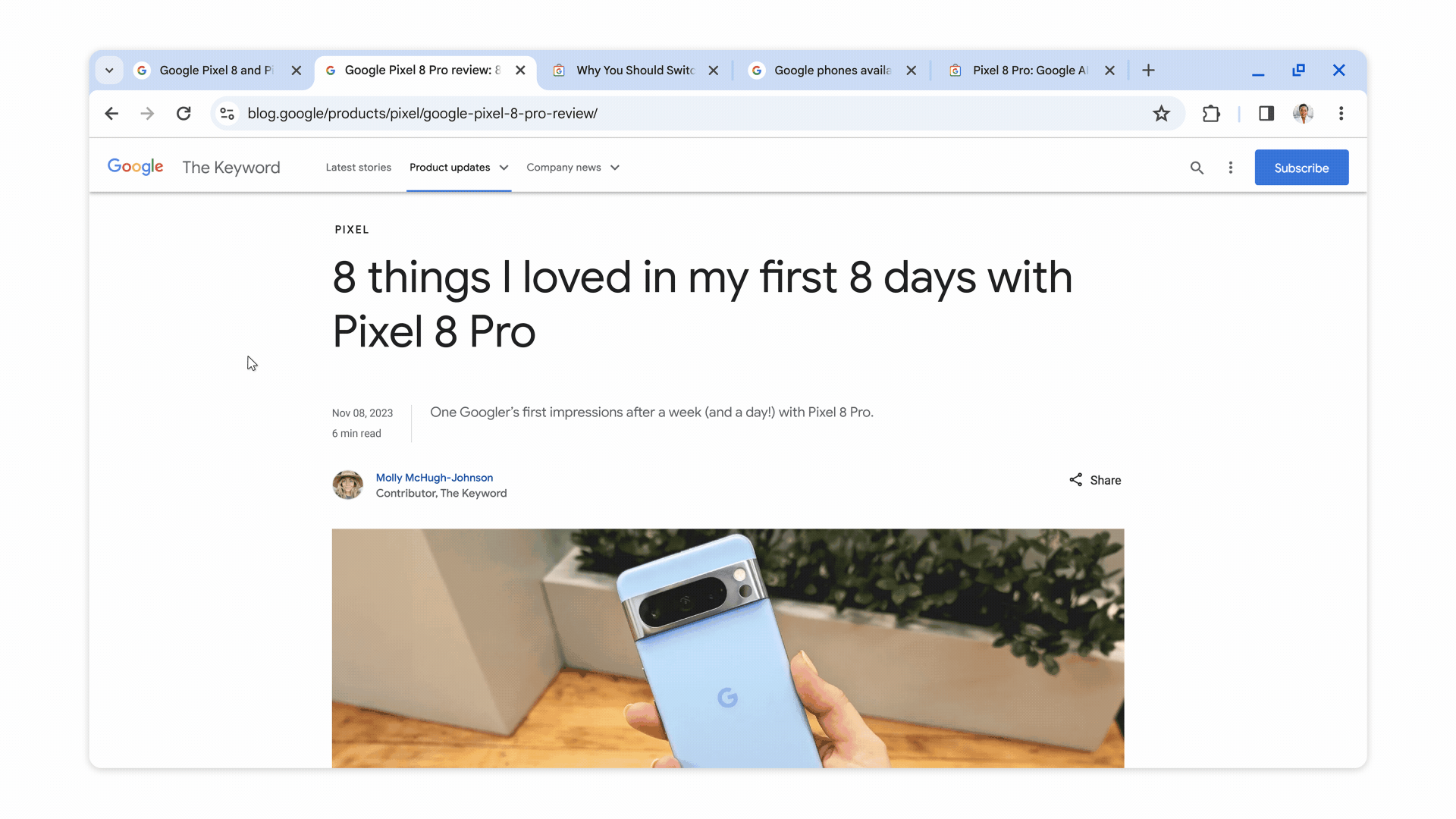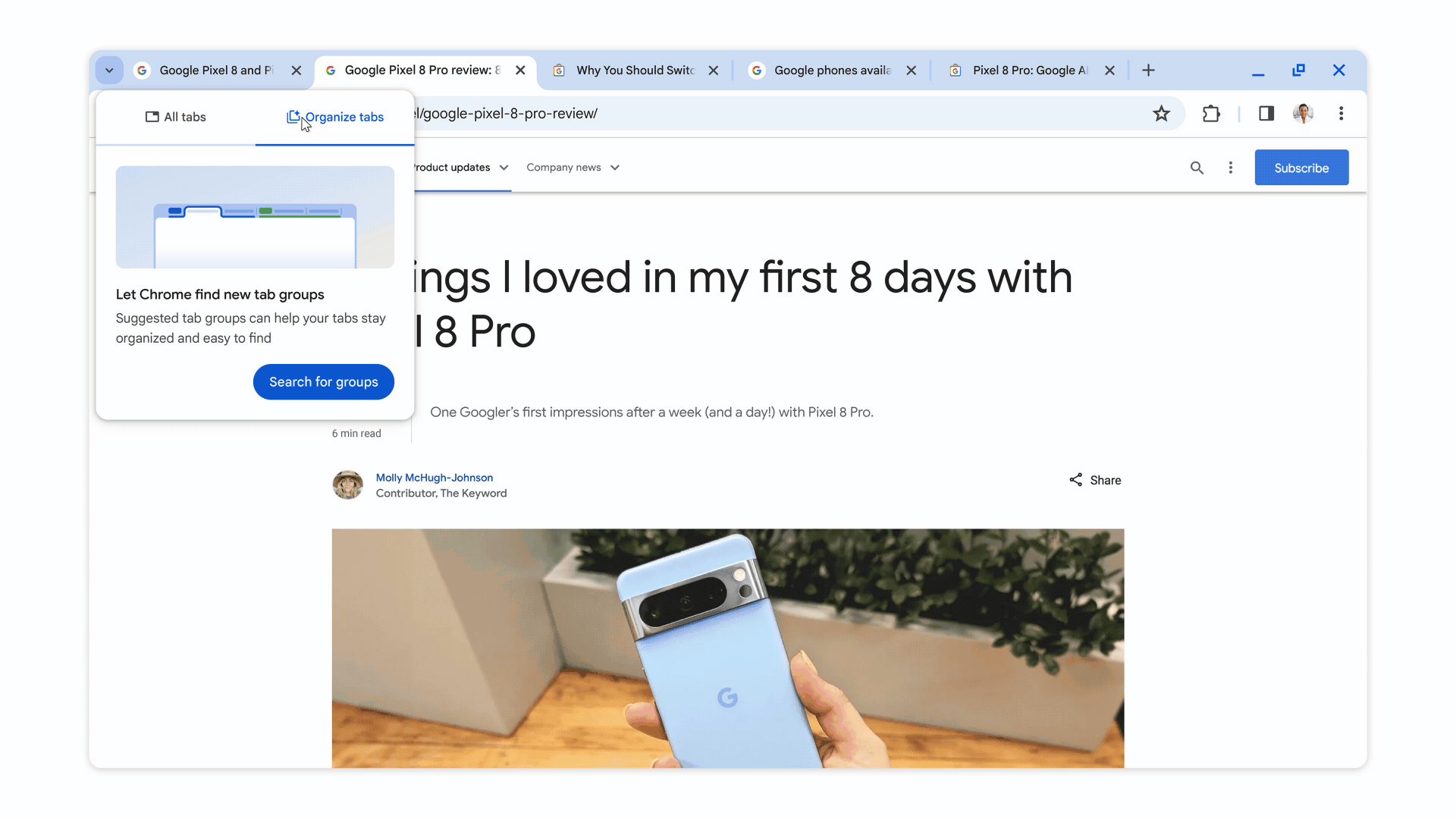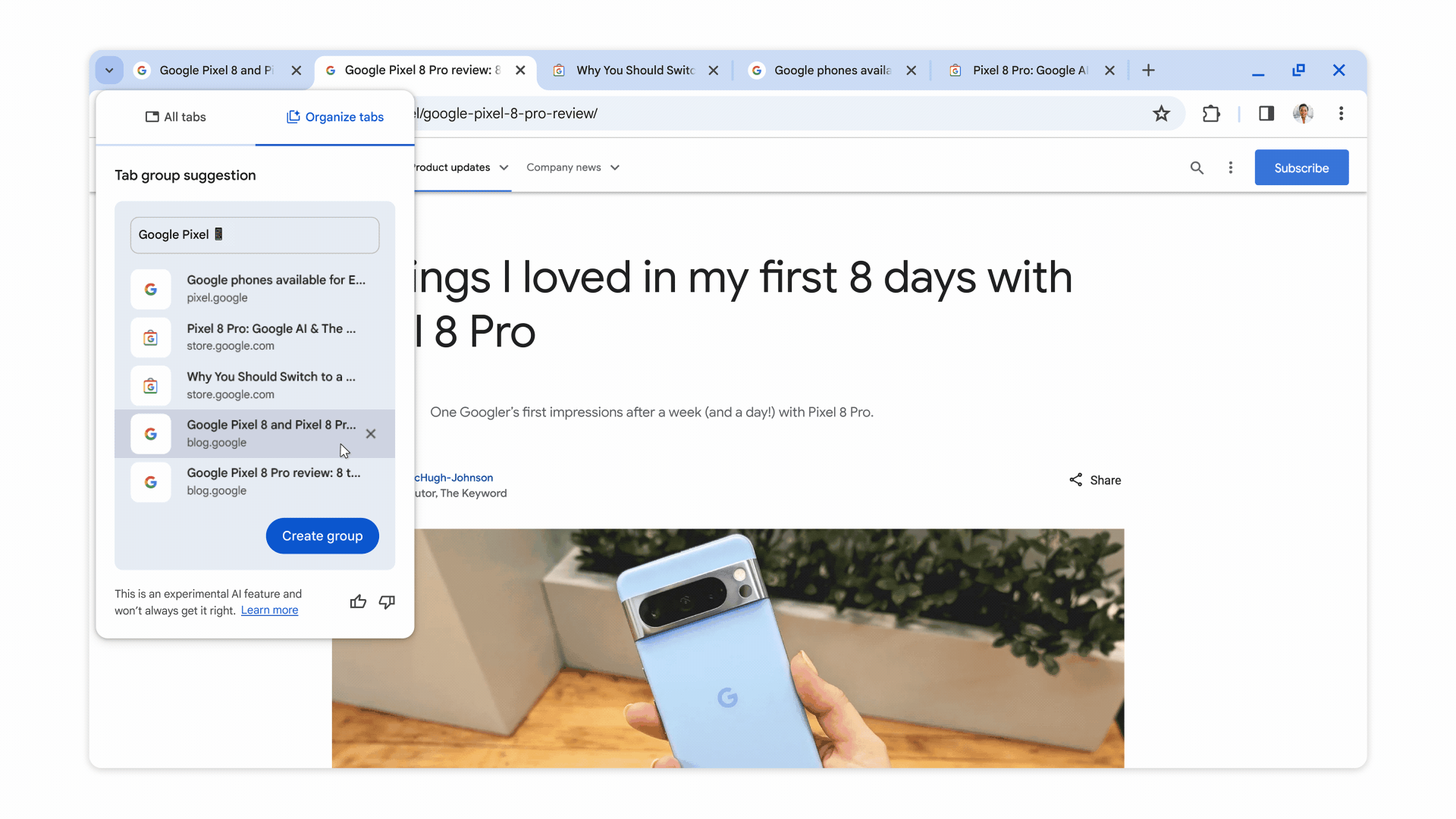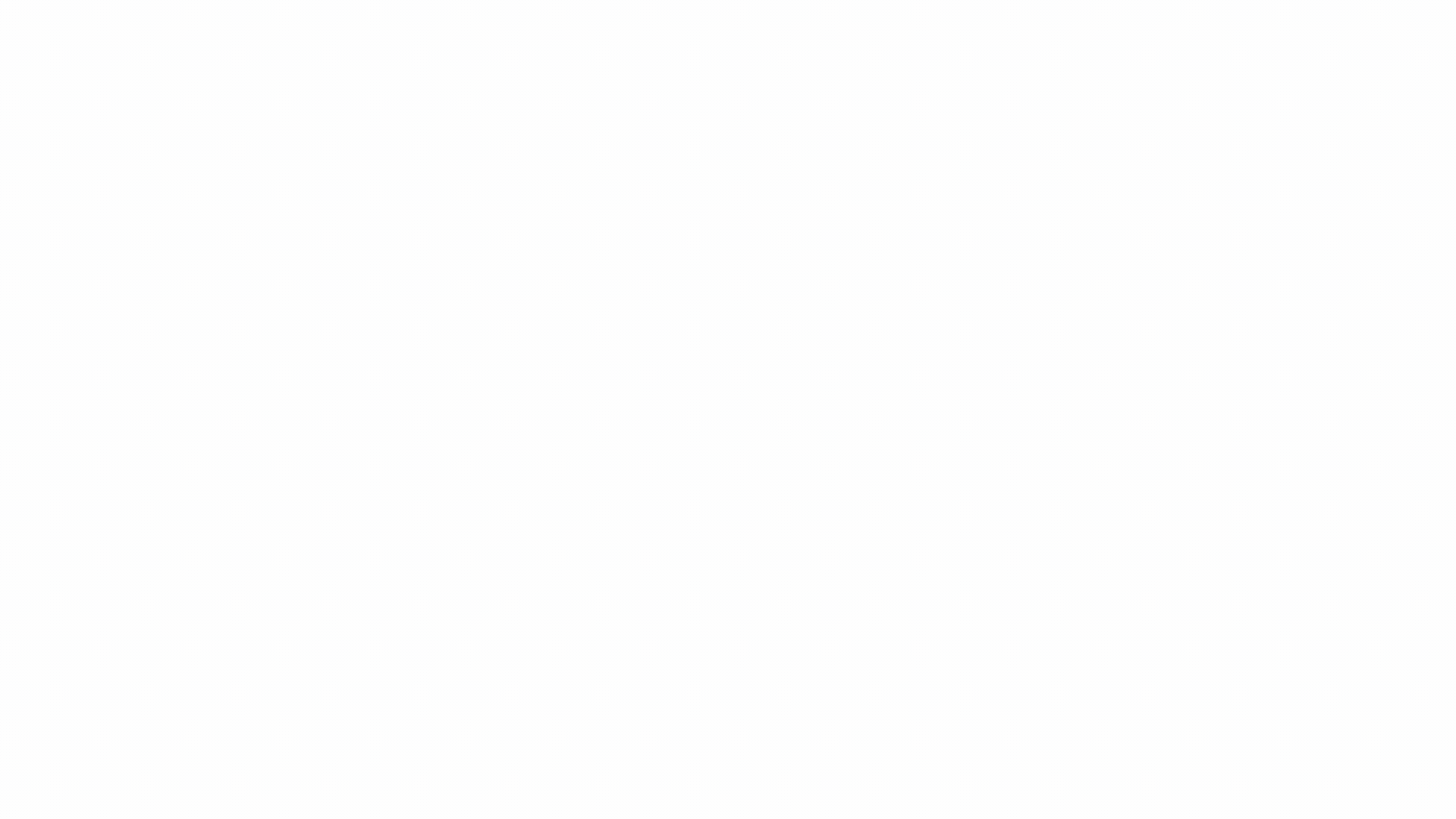
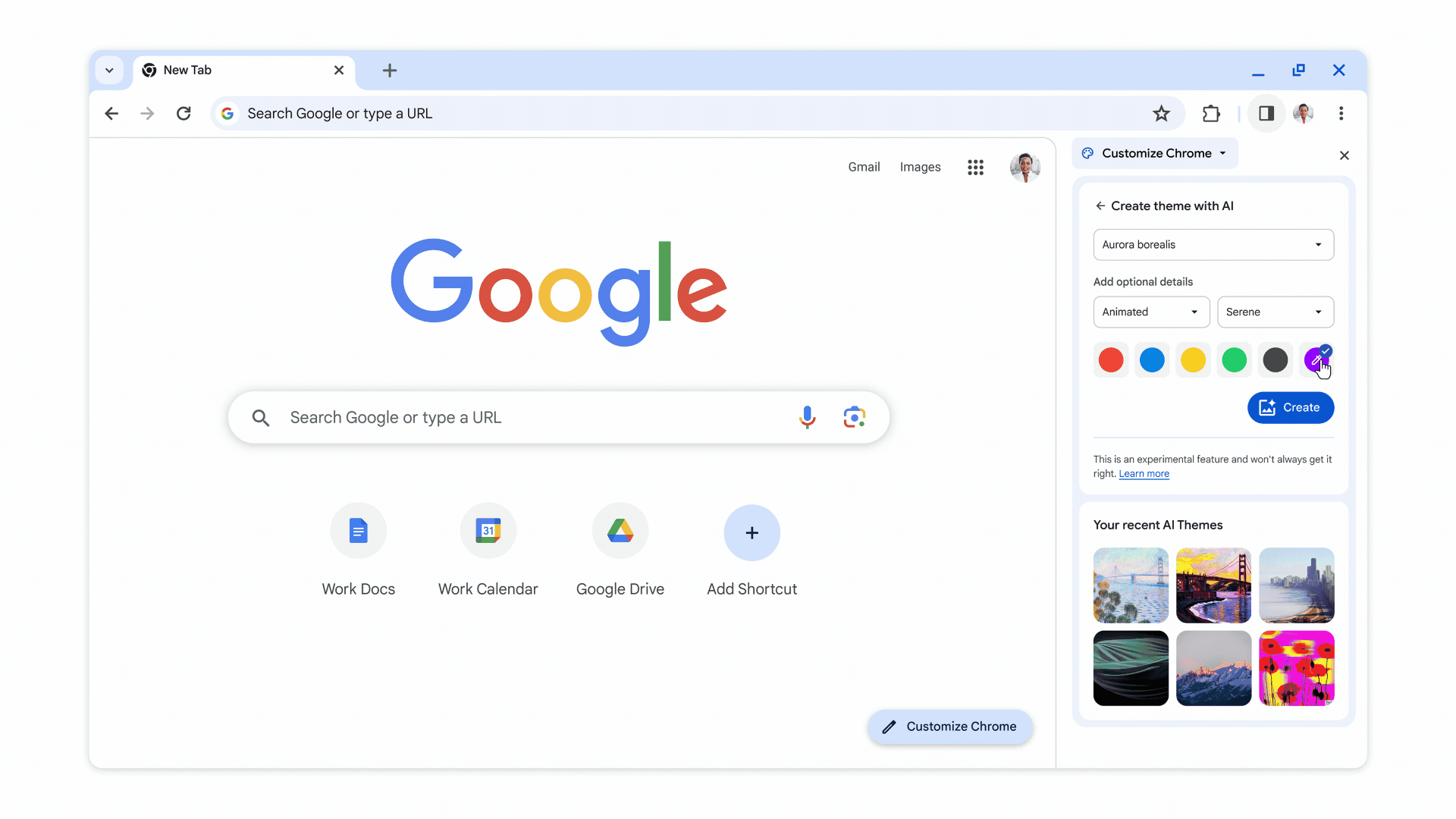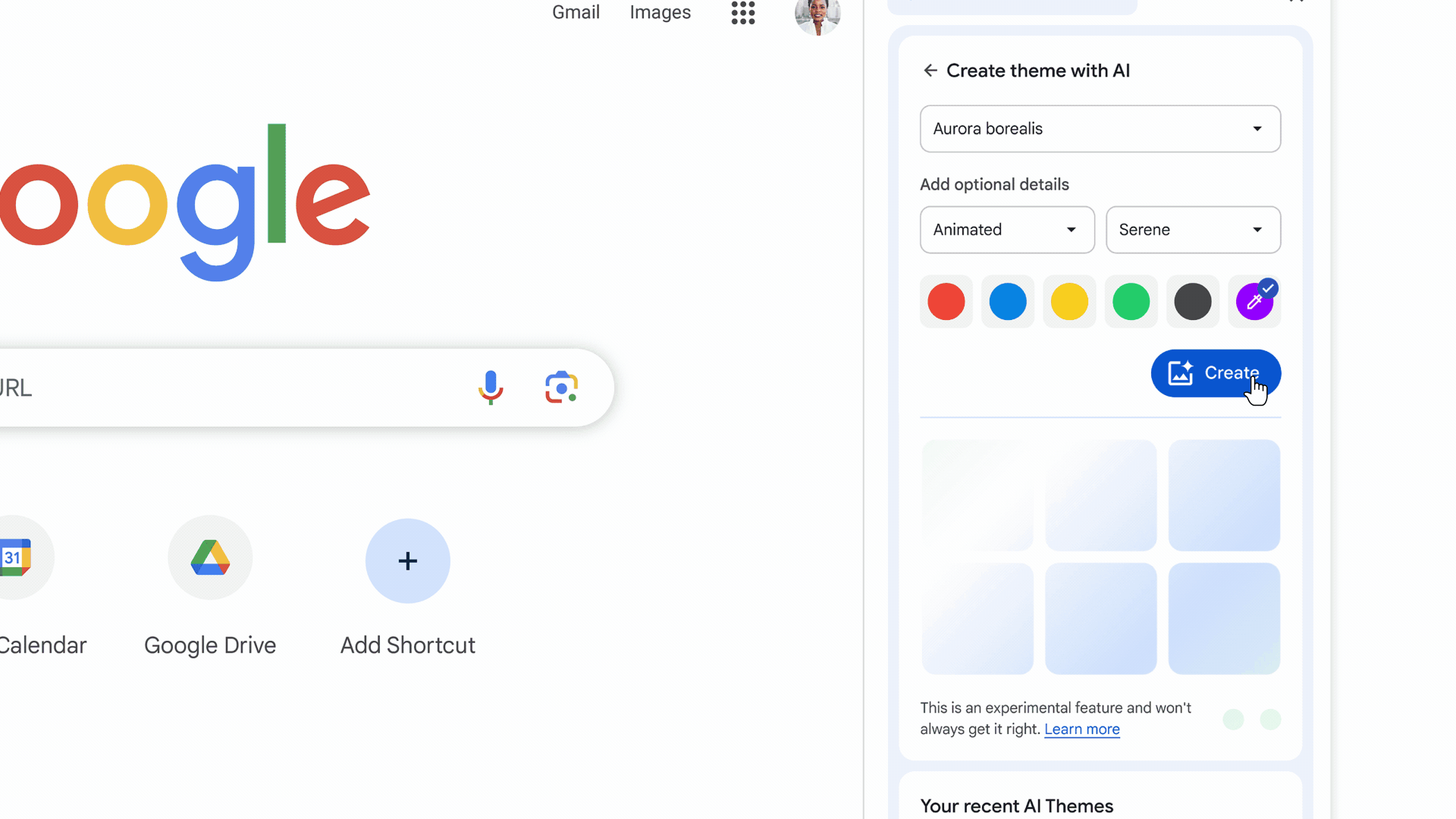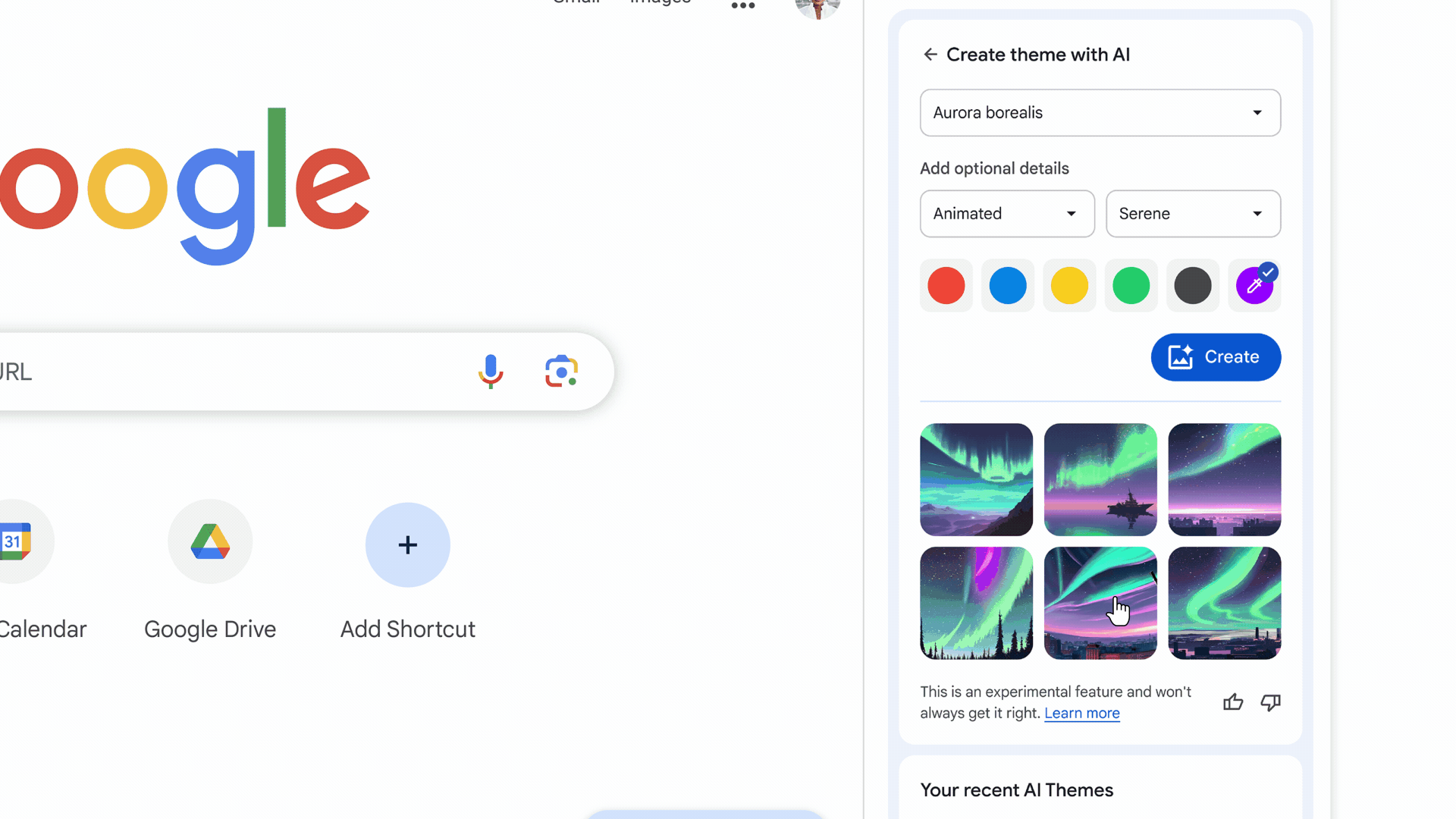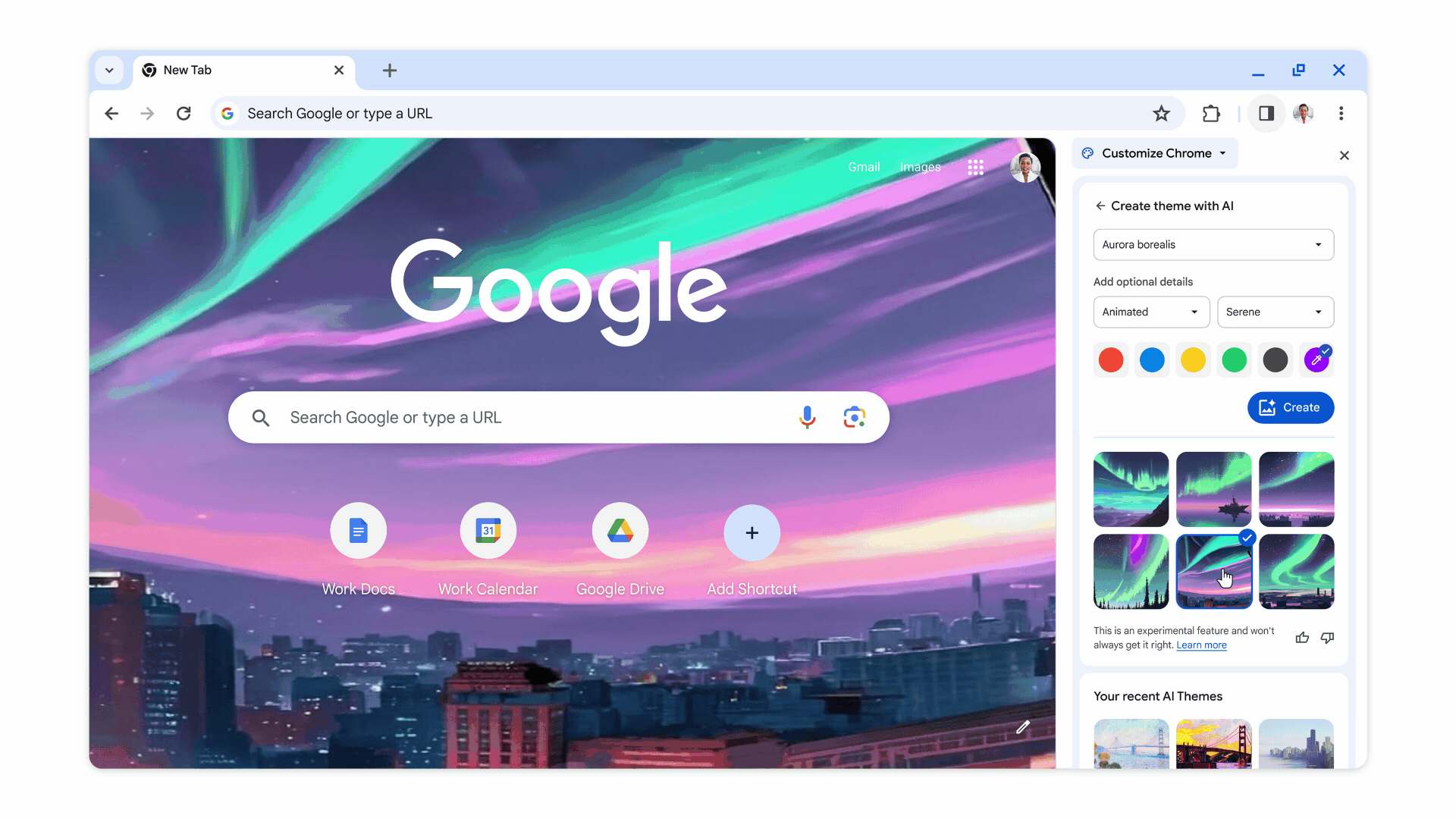
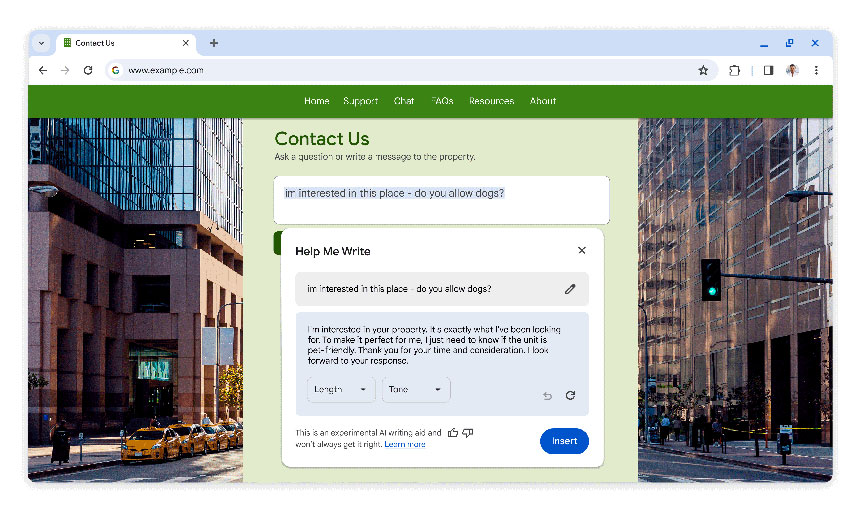
When turned on, these experimental AI features organize tabs into groups, create custom themes, and provide help with writing on the web in forum posts and online reviews, as shown in the images below.
Chrome will also suggest names and emojis for the tab groups it creates to make them easier to find. This feature is intended to assist when users are online shopping, researching, trip planning, or doing other tasks that tend to leave a lot of open tabs.
In addition to AI-generated themes, users can also customize Chrome with photos uploaded or themes from Chrome Web Store’s collections.
The features join other AI-powered and machine learning (ML) tools already available in Chrome, like its ability to caption audio and video, protect users from malicious sites via Android’s Safe Browsing feature in Chrome, silence permission prompts, and summarize web pages via the “SGE while browsing” feature.
In 2025, Chrome will be updated with more AI and ML features, including through integrations with its new AI model, Gemini, according to Google.
.




![Zuckerberg Says Meta Wants to Develop an Open-Source AGI [Video]](https://cms.iblnews.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/zuck.jpg)


![“Build Domain-Specific Language Models,” Said Coursera’s CEO in Davos [+Jan 18 Update]](https://cms.iblnews.org/wp-content/uploads/2024/01/coursera.jpg)

