IBL News | New York
ACI Learning, a Denver, Colorado-based IT, cyber, and audit training leader, launched myACI, a personalized enterprise learning system for IT teams.
It’s a skills-building platform that provides an adaptive learning experience, supports industry-recognized certifications, and includes an AI-powered career mentor.
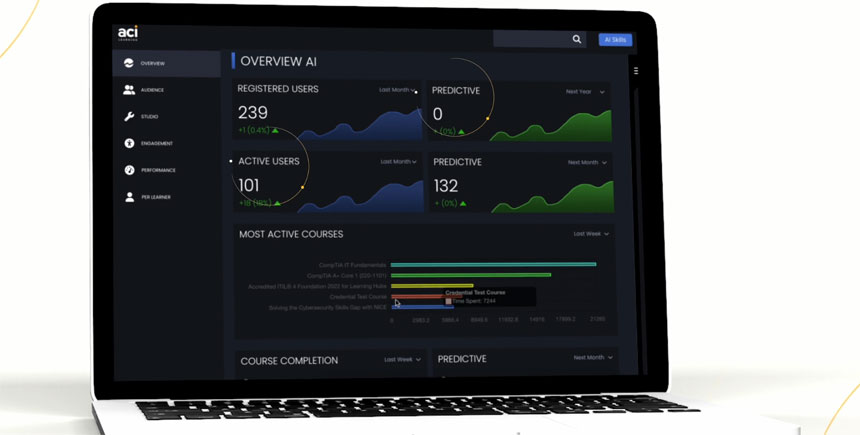
The company said that the company has an 80% content completion rate.
“With myACI, we are shifting the company’s market-defining content offerings to a full-service, scalable solution enabling individuals and organizations to leverage amazing training, real-world labs, and integrated AI mentoring to understand and gain the critical skills needed to succeed today,” said Brett Shively, CEO of ACI Learning.
With over 1,000 courses and labs in IT, cyber, and audit, ACI Learning serves over 3,000 customers and 250,000 subscribers worldwide.
According to the company, key features of myACI include:
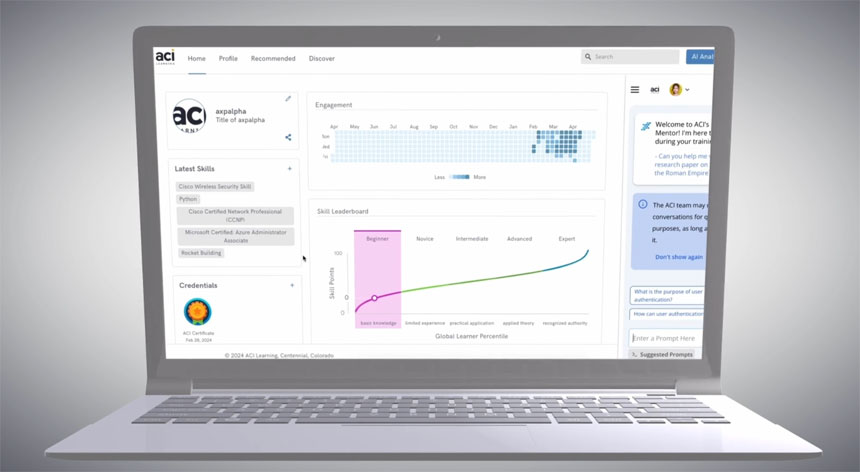
- “AI Mentor: This innovative tool empowers learners to identify skill gaps for targeted growth, engage deeply with personalized learning insights, and build custom course curriculum and content tailored to individual needs — without leaving the platform.
- Skill Labs: With over 5,000 custom labs, the market-leading Skill Labs offer a dynamic and immersive environment to provide learners with hands-on practice and real-world application. Unlike traditional simulations, Skill Labs replicate authentic scenarios and challenges, allowing learners to hone skills in a genuine and practical setting.
- Leader Dashboards and Reporting: A comprehensive view for leaders to track learners’ progress, customize training paths, and add internal training modules. The platform also allows organizations to upload internal training modules and specialized learning paths tailored to team members’ needs.
- Gamified Learning: A fun and motivating way to track progress and achievements, encouraging continuous learning and engagement. Gamification features include skill points, badges, and credentials.
- Secure Integrations: myACI securely integrates with all existing technologies, including any existing Learning Management Systems (LMS), and can scale to any size team and organization.
- Improved Content Catalog: A thoughtfully designed catalog that curates content based on individual preferences and past use, making it easier for users to find relevant learning paths.”