IBL News | New York
AI spending surged to $13.8 billion in 2024 from $2.3 billion in 2023 as enterprises embed AI at the core of their business strategies and daily work, according to a study conducted by Menlo Ventures.
This research, titled “2024 State of Generative AI in the Enterprise Report,” done after surveying 600 U.S. enterprise IT decision-makers, points out that we are still in the early stages of a large-scale transformation.
This spending will continue: 72% of decision-makers anticipate broader adoption of generative AI tools soon.
Investments in the LLM foundation model still dominate spending, but the application layer segment to optimize workflows is now growing faster.
These app layer companies—mostly in highly verticalized sectors—leverage LLM’s capabilities across domains to unlock new efficiencies. Enterprise buyers will invest $4.6 billion in generative AI applications in 2024, an 8x increase from the $600 million invested in 2023.
The use cases that deliver the most ROI through enhanced productivity or operational efficiency are:
• Code copilots, such as GitHub Copilot, Cursor, Codeium, Harness, and All Hands.
• Support knowledge-based chatbots for employees, customers, and contact centers. Aisera, Decagon, Sierra, and Observe AI are some of the examples.
• Enterprise search, retrieval, data extraction, and transformation to unlock the knowledge hidden within data silos. Solutions like Glean and Sana connect to emails, messengers, and document stores, enabling unified semantic search across systems.
• Meeting summarization to automate note-taking and takeaways. Examples are Fireflies.ai, Otter.ai, Fathom, and Eleos Health.
AI-powered autonomous agents capable of managing complex, end-to-end workflow processes are emerging and can transform human-led industries. Forge, Sema4, and Clay are some tools.
When deciding to build or buy, 47% of solutions are developed in-house, while 53% are sourced from vendors. Often, organizations discover too late that they have underestimated the difficulty of technical integration, scalability, and ongoing support.
Most customers (64%) prefer buying from established vendors, citing trust.
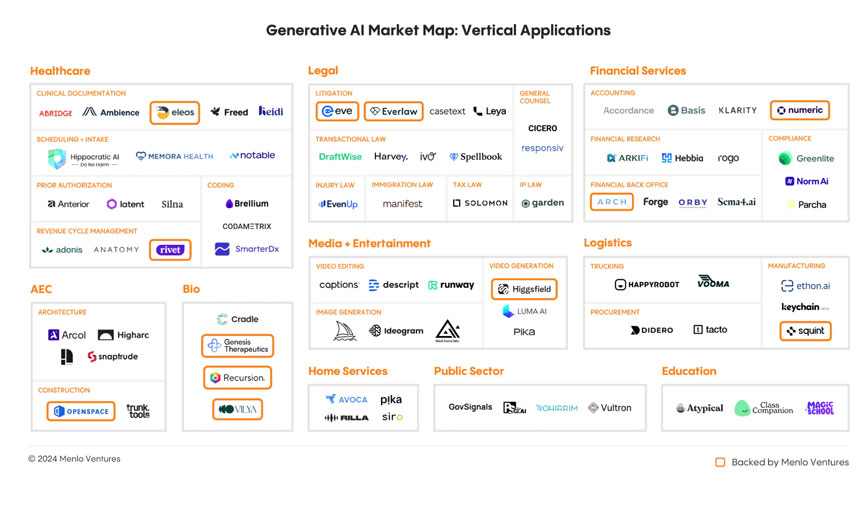
The leading vertical AI applications are:
• Healthcare, with examples like Abridge, Ambience, Heidi, Eleos Health, Notable, SmarterDx, Codametrix, Adonis, and Rivet.
• Legal, with examples like Everlaw, Harvey, Spellbook, EvenUp, Garden, Manifest, and Eve.
• Financial Services, with examples like Numeric, Klarity, Arkifi, Rogo, Arch, Orby, Sema4, Greenlite, and Norm AI.
• Media and entertainment, with examples like Runway, Captions, Descript, Black Forest Labs, Higgsfield, Ideogram, Midjourney, and Pika.
Rather than relying on a single provider, enterprises have adopted a multi-model approach, typically deploying three or more LLM in their AI stacks, routing to different models depending on the use case or results.
To date, close-source solutions underpin the vast majority of usage, with Meta’s Llama 3 holding at 19%, according to the Menlo Ventures research.
Regarding architectures for building efficient and scalable AI systems, RAG (retrieval-augmented generation) dominates with 51% adoption, while fine-tuning of production molded is only 9%. Agentic architectures, which debuted this year, power 12% of implementations.
Databases and data pipelines are needed to power RAG. Traditional databases like Postgres and MongoDB remain common, while AI-native vector databases like Pinecone gain ground.
Menlo Ventures made three predictions for what lies ahead:
1. Agentic automation will drive the next wave of transformation, tackling complex, multi-step tasks beyond the current systems of content generation and knowledge retrieval. Examples are platforms like Clay and Forge
2. More incumbents will fall. Chegg saw 85% of its market cap vanish, while Stack Overflow’s web traffic halved. IT outsourcing firms like Cognizant, legacy automation players like UiPath, and even software giants like Salesforce and Autodesk will face AI-native challengers.
3. The AI talent drought will intensify. AI-skilled enterprise architects will notably increase their salaries.
Squint, Typeface…
:no_upscale():format(webp)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/25759091/Anthropic_Claude_custom_style.gif)